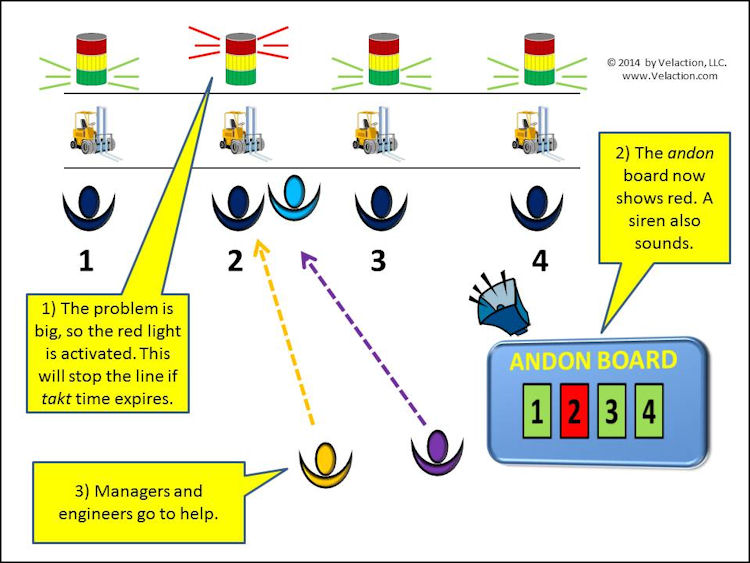
Andon Board
An andon light, in its most common use, is a status indicator for a work area. It generally has green, yellow, and red lights in a stack. As the operator experiences abnormal conditions, he or she lights a different color. The colors have meaning. Yellow might be a call for Read more…