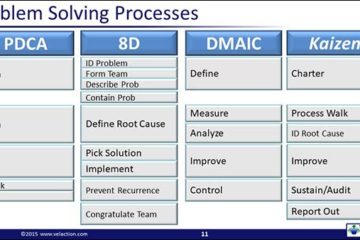
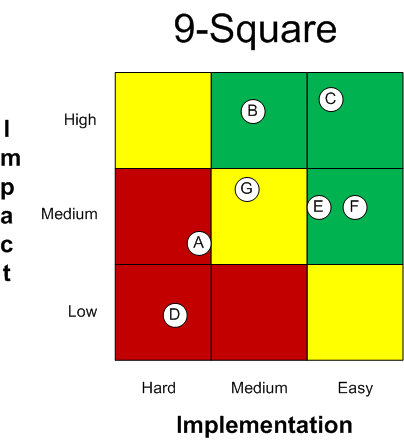
Gemba
Literally translated, “gemba” means “the real place”. To experienced practitioners of Lean, this means the place where work is actually being done or value is being created. NOTE: You may also hear the term as genba, with an “N”. Those who focus more on the traditional manufacturing roots of Lean Read more…