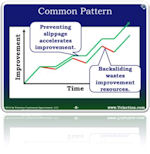
Backsliding
Backsliding it the act of reverting to a pre-improvement process. If you were to plot improvement over time on a run chart, backsliding would give the curve a saw-tooth look to it. A gain followed by a drop, followed by a gain and another drop. Backsliding is reduced by standardization Read more…