Expectations
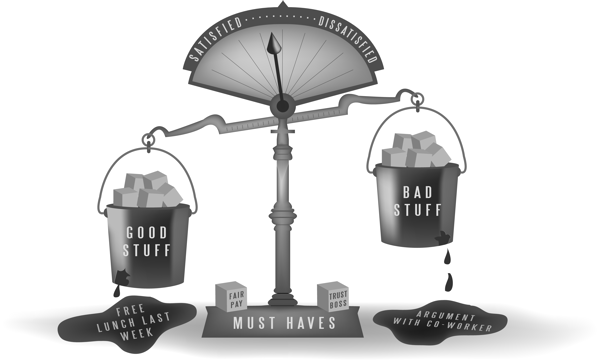
Setting expectations is part of the relationship building process. Whether between a boss and a subordinate, or a Lean advocate and the rest of the company, relationships are formed by what one party expects from the other. One of the things that sets the human mind apart from that of Read more…