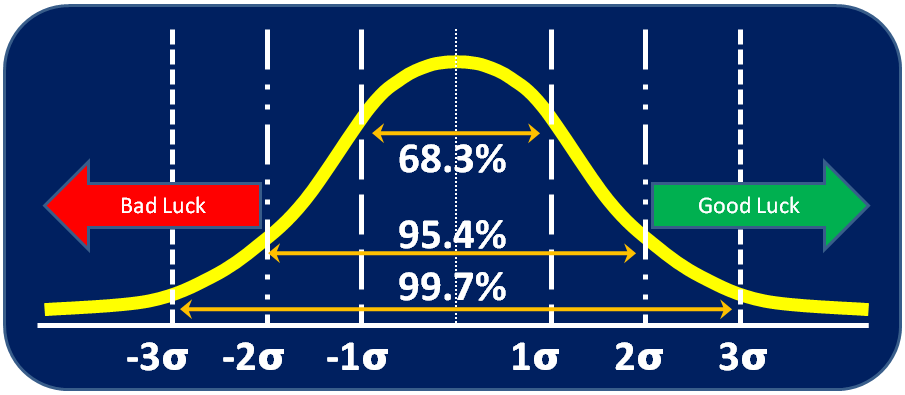
Objective vs. Subjective
Being able to recognize objective vs. subjective information is an important skill for individuals in Lean companies. Objective vs. Subjective Definitions Objective: Information or data that is based in fact. Often numerical. Can be verified by an independent third party. Example: Math tests. Subjective: Information or opinions that are open Read more…